Can Hepatitis B Be Cured? The Truth Patients Are Searching
A detailed explanation of acute and chronic hepatitis B, treatment options, and long-term management Hepatitis B is a viral infection …
Read More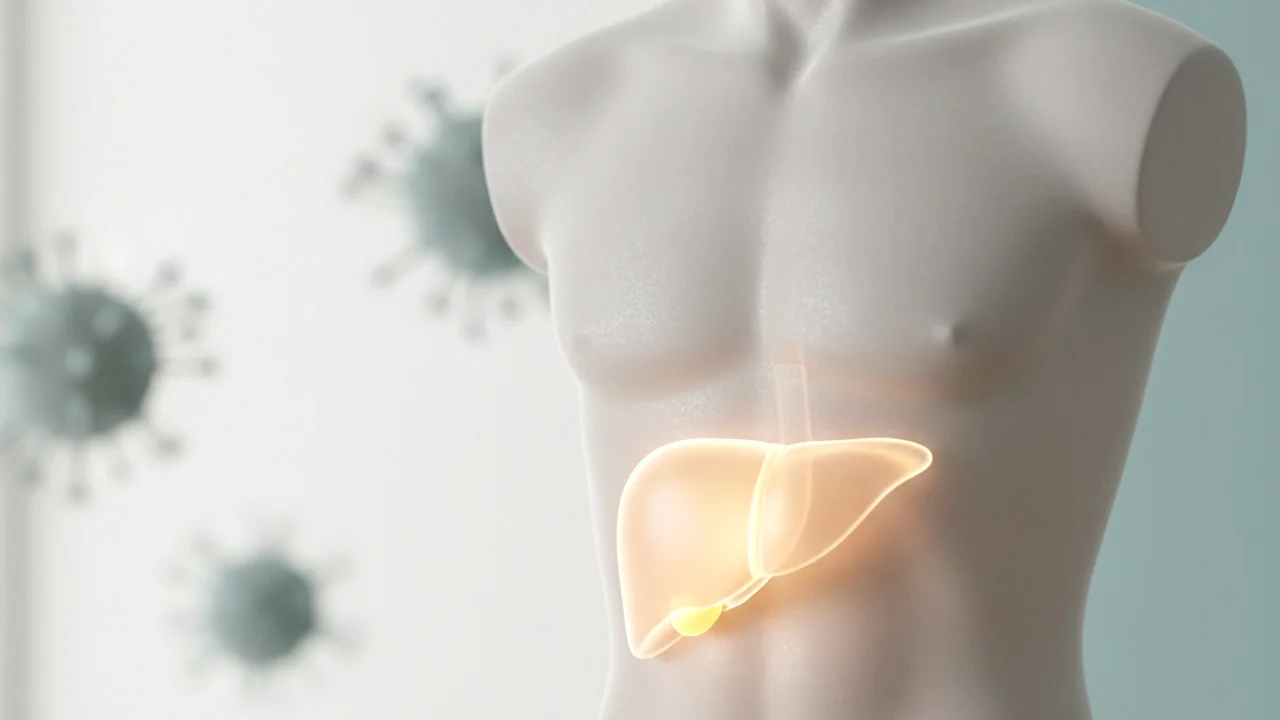
A detailed explanation of acute and chronic hepatitis B, treatment options, and long-term management
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus and can range from a short-term illness to a long-term chronic condition. Because hepatitis B is widely discussed in relation to liver damage and cancer risk, many people understandably ask “Can Hepatitis B Be Cured?”
The answer depends on whether the infection is acute or chronic. Understanding the difference between these two forms is essential when discussing cure and treatment outcomes.
Hepatitis B is an infection that targets liver cells. The virus spreads through contact with infected blood or body fluids. This can occur through unprotected sexual contact, sharing needles, from mother to baby during childbirth, or through unsafe medical procedures in some parts of the world.
Once inside the body, the virus infects liver cells and begins to multiply. The immune system responds by attacking infected cells, which can cause inflammation and liver damage.
Acute hepatitis B refers to the early stage of infection, usually within the first six months after exposure. Many adults who become infected experience mild symptoms or none at all. Some may develop fatigue, nausea, abdominal discomfort, jaundice, or dark urine.
In most healthy adults, the immune system successfully clears the virus from the body. When this happens, the infection resolves naturally and does not return. In these cases, hepatitis B is effectively cured because the virus is eliminated, and the person develops lifelong immunity.
Supportive care is usually all that is required during acute infection, as there is no specific antiviral cure needed for most people at this stage.
Chronic hepatitis B occurs when the virus remains in the body for longer than six months. This is more likely to happen in babies and young children who are infected, as their immune systems are less likely to clear the virus naturally.
In chronic hepatitis B, the virus persists in liver cells and may slowly cause inflammation and scarring. This can increase the risk of liver cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer if not properly managed.
Chronic hepatitis B cannot currently be completely cured in most cases, but it can be effectively controlled with treatment.
At present, there is no complete cure that removes the virus entirely from the body in most people with chronic hepatitis B. However, antiviral medicines can suppress the virus to very low levels, preventing liver damage and significantly reducing the risk of complications.
These treatments allow many people with chronic hepatitis B to live long and healthy lives. Research is ongoing, and scientists are working toward developing therapies that may achieve a complete cure in the future.
Treatment depends on the level of viral activity and the condition of the liver. Some people with chronic hepatitis B may not require immediate treatment but will need regular monitoring. Others may be prescribed antiviral medication to reduce viral replication and protect the liver.
Treatment is usually long-term, and regular blood tests and liver scans are used to monitor progress and prevent complications.
Acute hepatitis B in adults often clears on its own, meaning the body successfully removes the virus without long-term effects. However, chronic hepatitis B does not usually resolve spontaneously and requires ongoing monitoring or treatment.
Early diagnosis is crucial for preventing serious liver damage.
Hepatitis B is preventable through vaccination. The hepatitis B vaccine provides long-term protection and is recommended for babies, healthcare workers, and individuals at increased risk of exposure.
Vaccination remains one of the most effective ways to reduce the global burden of hepatitis B.
Anyone who believes they may have been exposed to hepatitis B should seek medical advice promptly. Early testing allows appropriate monitoring and management.
People diagnosed with hepatitis B should attend regular follow-up appointments to assess liver health and determine whether treatment is required.
Hepatitis B can be completely cured in most adults who develop acute infection, as the immune system clears the virus naturally. However, chronic hepatitis B cannot currently be fully cured in most cases, though it can be effectively controlled with antiviral treatment.
With proper monitoring, treatment, and vaccination strategies, the risks associated with hepatitis B can be significantly reduced, allowing individuals to maintain good long-term liver health.
“Always polite and delivers medication on time. Absolutely love the service they provide and great staff. Keep up the good work ????”
“A fantastic pharmacy. Efficient, helpful staff who deliver within a few hours of prescription being prescribed or less. Absolutely amazing service.”
“Can highly recommend this service, the delivery is so speedy and always reliable, delivered by hand to the door, just amazing, thank you.”
A detailed explanation of acute and chronic hepatitis B, treatment options, and long-term management Hepatitis B is a viral infection …
Read MoreA detailed explanation of safety, risks, and managing cough during pregnancy Cough is a common symptom during pregnancy, often caused …
Read MoreA detailed explanation of the link between earwax buildup and ringing in the ears Tinnitus is a condition where a …
Read MoreClick one of our contacts below to chat on WhatsApp